HI (aq) Phosphorous acid H 3 PO 3 Carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 Sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 Formic acid HCOOH Name each of the following acids HClO 4 perchloric acid HCOOH formic acid H 3 PO 4 phosphoric acid HCl (aq) hydrochloric acid H 3 BO 3 boric acid H 2 SO 4 sulfuric acid HNO 2 nitrous acid HI (aq) hydroiodic acid CH 3 COOH acetic acidHydrochloric acid HBr (strong acid) Hydrobromic acid HI (strong acid) HydroIodic acid HClO4 (strong acid) Perchloric acid H2SO4 (strong acid) (only the first proton is strong) Sulfuric AcidElectrolytes are substances which, when dissolved in water, break up into cations (pluscharged ions) and anions (minuscharged ions) We say they ionizeStrong electrolytes ionize completely (100%), while weak electrolytes ionize only partially (usually on the order of 1–10%) That is, the principal species in solution for strong electrolytes are ions, while the principal specie in solution

Ppt Strong Acids Vs Weak Acids Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Hi strong or weak acid or base
Hi strong or weak acid or base-This means that a weak acid does not donate all of its hydrogen ions (H ) in a solution Weak acids have very small values for K a (and therefore higher values for pK a ) compared to strong acids, which have very large K a values (and slightly negative pK a values)Start studying Strong/Weak Acids and Bases Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Search Create HI strong acid HNO₃ weak acid (ascorbic acid) H₂C₆H₆O₆




Classify The Compounds As Strong Acids Or Weak Acids H2co3 Clutch Prep
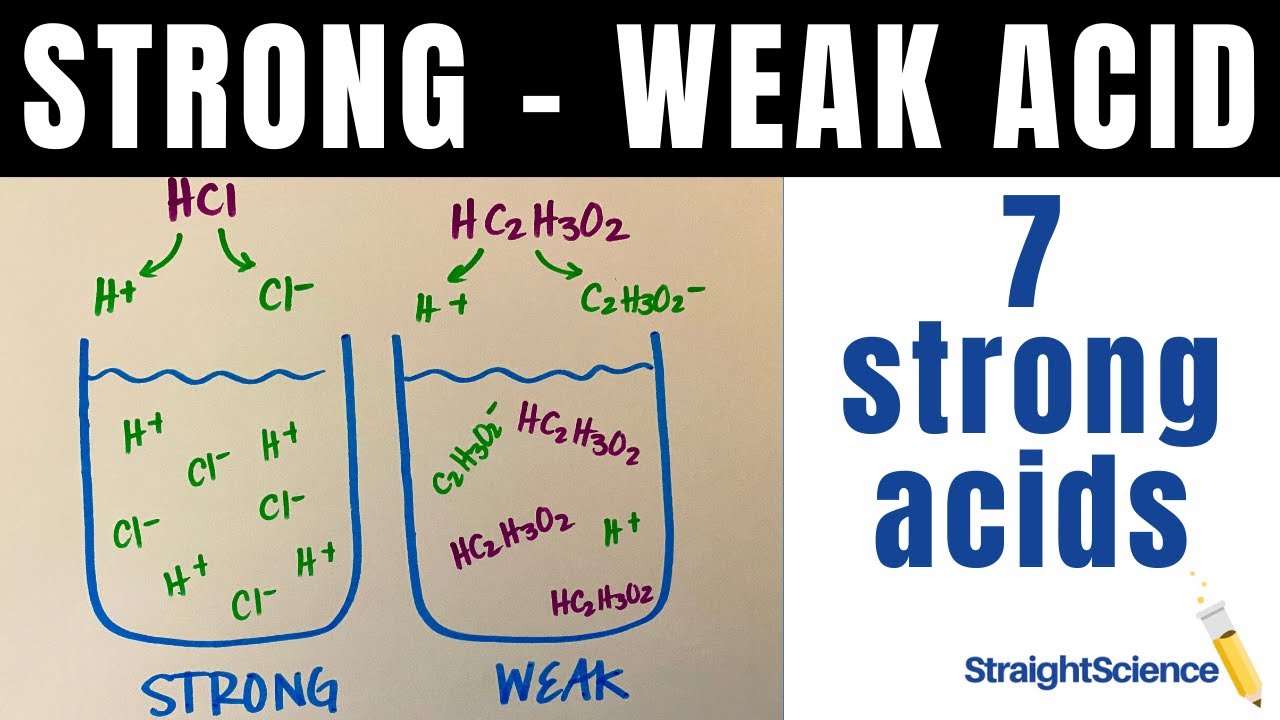
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases Many hardware stores sell "muriatic acid" a 6 M solution of hydrochloric acid HCl(aq) to clean bricks and concrete Grocery stores sell vinegar, which is a 1 M solution of acetic acid CH 3 CO 2 H Although both substances are acids, you wouldn't use muriatic acid in salad dressing, and vinegar is ineffective in cleaning bricks or concreteAcid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula, to dissociate into a proton, , and an anion, The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (), perchloric acid (), nitric acid and sulfuric acid () A weak acid is only partially dissociated, withIn chemistry, neutralization or neutralisation (see spelling differences), is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react quantitatively with each other LIST ACID NH4ClO4 NH4Cl HBrO (WEAK) H2PO4H3PO3 (WEAK) HNO3 (STRONG) HCl (STRONG) H2S (WEAK) H2SO4 (STRONG) H3PO4 (WEAK) H2CO3 (WEAK) HBr (STRONG HI (STRONG) HClO4 (STRONG) HClO3
Example 6 Identify each acid or base as strong or weak HCl;And nitric acid, HNO3, is a strong electrolyte Also Know, is potassium iodide A electrolyte? Solution NaOH is a strong base but H 2 C 2 O4 is a weak acid since it is not in the table Therefore, this is a weak acidstrong base reaction which is explained under the link, titration of a weak acid with a strong base
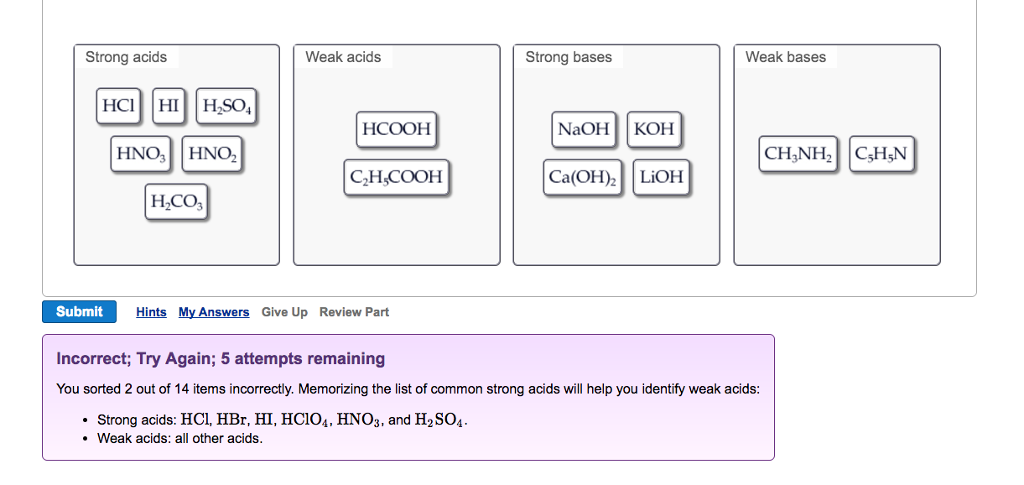
Classify each substance as a strong acid, strong base, weak acid,or weak baseStrong Acid Question Classify each substance as a strong acid, strong base, HI HCl H 2 SO 4 Weak Acid HClO 4 HCOOH HF HCN HNO 2 CH 3 COOH Strong Base Ca(OH) 2 LiOH NaOH KOH CsOH (CH 3) 2 NH Ba(OH) 2 Weak Bases NH 3 CH 3 NH 2 Please, let meSee the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Show transcribed image textGeneral Rule for strong or weak acid/base Strong binary acids Only HCl, HBr, HI, all other binary acids are weak Strong oxyacids Ratio of O to H is 2 or greater For example H 2 SO 4 or HNO 3 Strong bases Hydroxides of groups 1 and 2 (except Be), all others are weak




Eurekly Strong And Weak Acids As Opposed To Strong Acids Weak Acids Do Not Completely Dissociate In Water Here They Are Ho2c2o2h Oxalic Acid H2so3 Sulfurous Acid
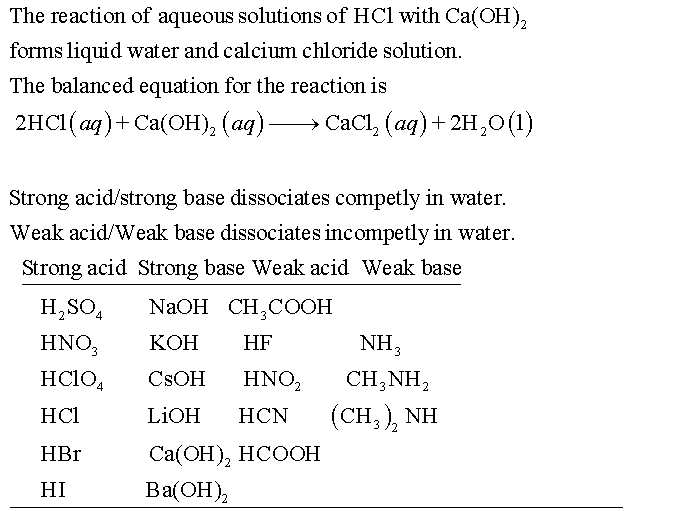



Classify Each Substance As A Strong Acid Strong Base Weak Acid Or Weak Base Home Work Help Learn Cbse Forum
Identify the strong and weak acids from the following list of acids hydrochloric acid, acetic add, formic acid, nitric acid asked in Class X Science by priya12 Expert (Hypochlorous acid, HClO, is a weak electrolyte; HCl is a strong acid;



Solved Classify Each Of The Following Substances As Either A Chegg Com




Classify The Compounds As A Strong Acid Weak Acid Strong Base Or Weak Base Strong Acid Homeworklib
To check If Nitric acid(HNO 3) a strong or weak, first we have to take a clear understanding of the differences between strong and weak acids A strong acid is generally a compound that dissociates completely or is 100% ionized in a solution to yield H ions which means no undissociated acid remains in the solution, all moles of acid completely break off and releaseClassify HI as a strong or weak acid or base Weak base strong acid strong base weak acid; In chemistry, there are seven "strong" acids What makes them "strong" is the fact that they completely dissociate into their ions (H and an anion) when they are mixed with waterEvery other acid is a weak acidBecause there are only seven common strong acids, it is easy to commit the list to memory




Strong Acid Solutions Video Khan Academy




Classify The Compounds As Strong Acids Or Weak Acids H2co3 Clutch Prep
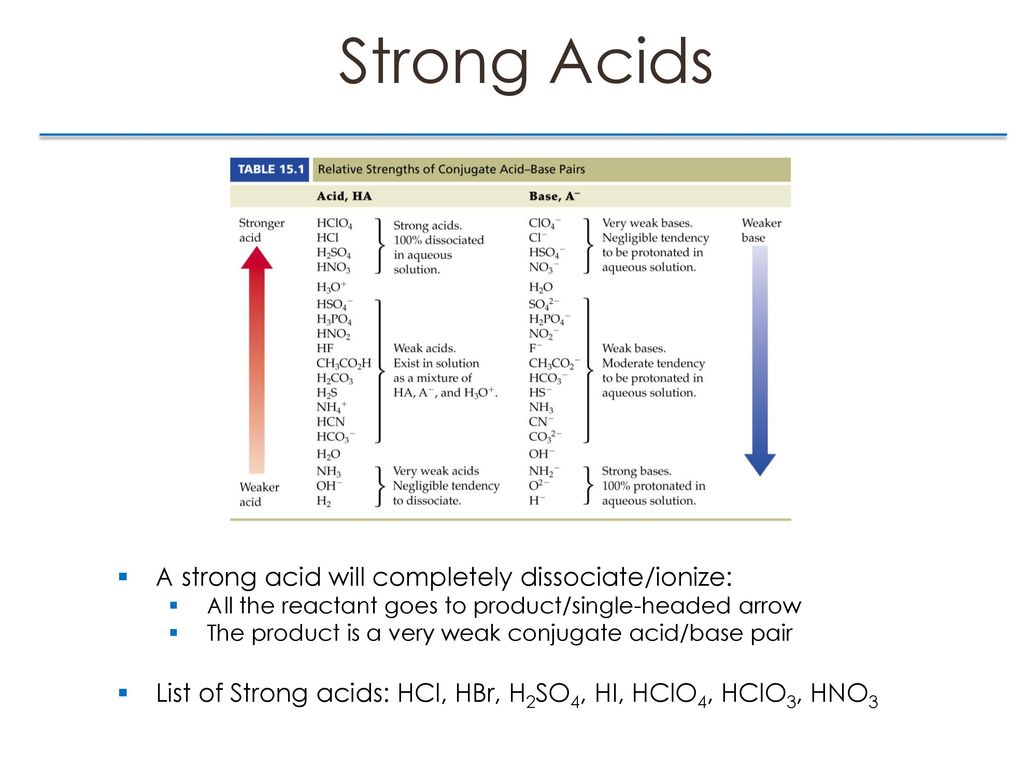
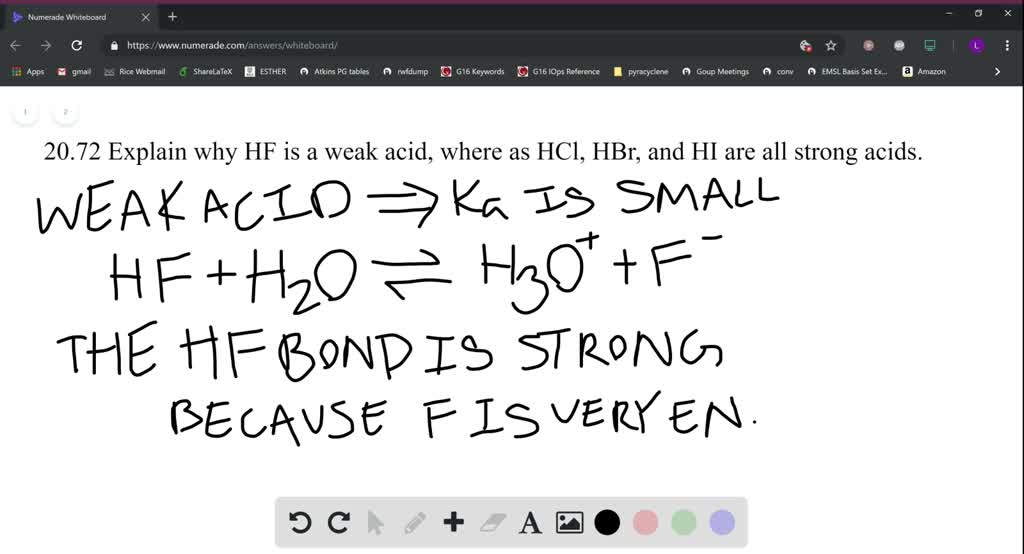
Because Mg(OH) 2 is listed in Table 122 "Strong Acids and Bases", it is a strong base The nitrogen in C 5 H 5 N would act as a proton acceptor and therefore can be considered a base, but because it does notChemistry Q&A Library Explain why HF is a weak acid, whereas HCl, HBr, and HI are all strong acids Explain why HF is a weak acid, whereas HCl, HBr, and HI are all strong acids closeAcid HA AKa pKa Acid Strength Conjugate Base Strength Hydroiodic HI IHydrobromic HBr BrPerchloric HClO4 ClO4Hydrochloric HCl ClChloric HClO3 ClO3Sulfuric (1) H2SO4 HSO4Nitric HNO3 NO3Strong acids completely dissociate in aq solution (Ka > 1, pKa < 1) Conjugate bases of strong acids are ineffective bases Hydronium ion H3O H2O 1 00




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid




Easy Way To Memorize The 7 Strong Acids And 6 Strong Bases Youtube
H2SO4, HClO3, HClO4, HNO3, HI, HCl, HBr are the strong acids Some weak acids are HF, HSO4, CH3COOH (acetic acid, found in vinegar), HCN, HIO, HBrO, HIO3, HNO2 A weak acid is the opposite ofWeak and strong should not be mistaken for dilute and concentrated A dilute acid has the acid molecules mixed with a large amount of water, so that there is only a low concentration of H ions Sucrose, C12H22O11, is a nonelectrolyte;
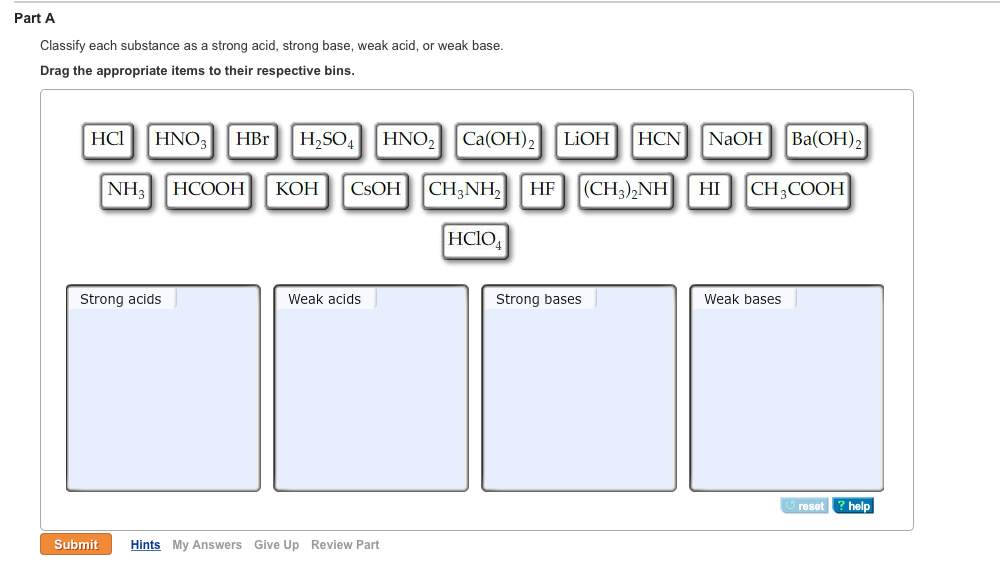



Solved Part A Classify Each Substance As A Strong Acid Chegg Com




Acids And Bases Three Definitions Arrhenius Acid Produces
Potassium iodide is a component in the electrolyte of dyes sensitized solar cells (DSSC) along with iodineNote Due to the fact that HI, HBr, HCl, H 2 SO 4, H 2 SeO 4, and HNO 3 virtually do not exist in undissociated form their first dissociation step is not explicitly contained in the thermodynamic database 1 Example calculations with strong acids are presented here Group 2 Acids with pK a > 0 (Weak Acids) In contrast to the strong acids with negative pK a values, acids with pK a > 0A weak acid is any acid that reacts with water (donates H ions) to a very small extent, usually less than 5 10% An aqueous solution of a weak acid in a state of equilibrium would consist mainly of the unionized form of the acid, and only a small amount of hydronium ions and of the anion (conjugate base) of the weak acid
/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)



List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids




Solution Order The Following Acids In Inc Clutch Prep
A weak acid is one that does not dissociate completely in solution;Mg(OH) 2 C 5 H 5 N; HF is a weak acid, but very dangerous (you may hear it etches glass, that's because the SiF bond is the strongest bond) HCl and the rest of them (HBr, HI) are all "strong acids" but HI is the strongest (see pKa's below) Due to poor orbital overlap (Iodine is much larger than H, and therefore the electrons are not very well shared, which imparts an extremely ionic character to




Strong And Weak Acids Bases Ppt Download




List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids
By analogy, a strong base A base that is 100% ionized in aqueous solution is a compound that is essentially 100% ionized in aqueous solution As with acids, there are only a few strong bases, which are also listed in Table 102 "Strong Acids and Bases (All in Aqueous Solution)" If an acid is not listed in Table 102 "Strong Acids and Bases (All in Aqueous Solution)", it is likely a weak Strong acids and bases ionize fully in an aqueous solution Weak acids and bases also ionize, but only partially and the reaction is reversible So how do we know if an acid or base is strong or weak? Whether HI is a strong acid or weak acid, depends on their tendency of losing proton ie, how easily it donates a proton Let us introduce the concept of the strong and weak acid Strong Acid and Weak Acid Those acids, which dissociate completely or 100 % in the solution are known as strong acids If the acids do not dissociate completely in
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)



List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids




Why Hydrogen Fluoride Is A Weaker Acid Than Hydrochloric Acid Find Acidic Order Of Hf Hcl Hbr Hi Youtube
Question Select the signal best answer Classify HI as a strong or weak acid or base Weak base strong acid strong base weak acid This problem has been solved!Answer (1 of 45) Iodine(I) has a bigger atomic radius than Fluorene (F) Due to its greater size, the distance between the valence electron and the nucleus is great than Fluorene Due to the large distance, when is makes a bond, the distance between There are two ways to determine whether HI is a strong or weak acid The first it to memorize the seven common strong acids For general chemistry courses t




Strong Acids Do Dissociate Completely Weak Acids Do Not Dissociate Completely The Strong Acids Are Hno 3 H 2 So 4 Hclhio 4 Hclo 4 Hbr Hclo 3 Hi Ppt Download




Acids And Bases Chapters 14 15 Common Acids
A simple way to determine strength is to add the acid or base to water—high reactivity means a stronger acid or base This reactivity is Once the strong acid has been ionized, the reaction stops and is not reversible Here is the reaction of ethanoic acid, a weak acid CH 3 COOH H 2 O ⇆ H 3 O CH 3 COONotice here that the reaction arrow points in both directions This means that the reaction proceeds in both directions, which isn't the case for strong acids A weak acid is an acid that partially dissociates into its ions in an aqueous solution or water The conjugate base of a weak acid is a weak base, while the conjugate acid of a weak base is a weak acid At the same concentration, weak acids have a higher pH value than strong




Lecture 9 Acid Base Equilibria I Strong Acids Hcl Hbr Hi Hno 3 H 2 So 4 Hclo 4 Ho N E O Weak Acid Ho N Eo 2 Strong Acid We Titrate With Strong Ppt Download




36 Which One Of The Following Is Not A Strong Acid Or A Weak Electrolyte A Hno Hci Hi Hf E Hcio Answer 37 The Is The Conjugate Species That Remains After
Reactions Hydroiodic acid reacts with oxygen in air to give iodine 4 HI O 2 → 2 H 2 O 2 I 2 Like other hydrogen halides, hydroiodic acid adds to alkenes to give alkyl iodides It can also be used as a reducing agent, for example in the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to anilines Cativa process The Cativa process is a major end use of hydroiodic acid, which serves as a co Main Difference – Strong vs Weak Acids An acid is a molecule or other species which can donate a proton or accept an electron pair in reactions Acids are classified into two groups known as strong acids and weak acids The main difference between strong and weak acids is that strong acids dissociate completely in aqueous solutions whereas weak acidsHF Weak Acid 813% HI Strong Acid 100% HBr Strong Acid 100% H2O Weak Acid 001% HCl Strong Acid 100% SUMMARY Strong acids have a very high dissociation rate and weak acids have a very low dissocation rate PART 3 Exend (30 minutes) To continue allowing your students to practice and review Acid Strength, assign the Extend Activity on




Strong And Weak Acids And Bases Biology




Super Trick To Learn Example Of Strong Acid Strong Base Weak Acid Weak Base Type Of Salt Ionic Youtube
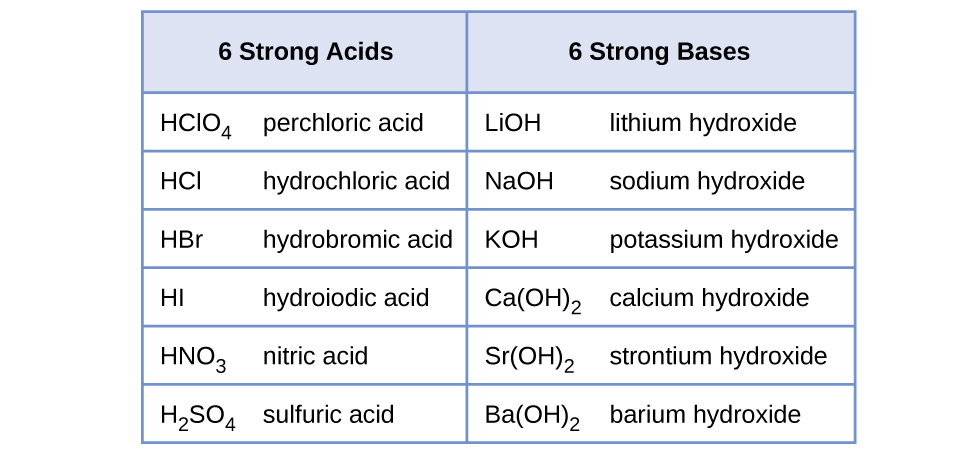
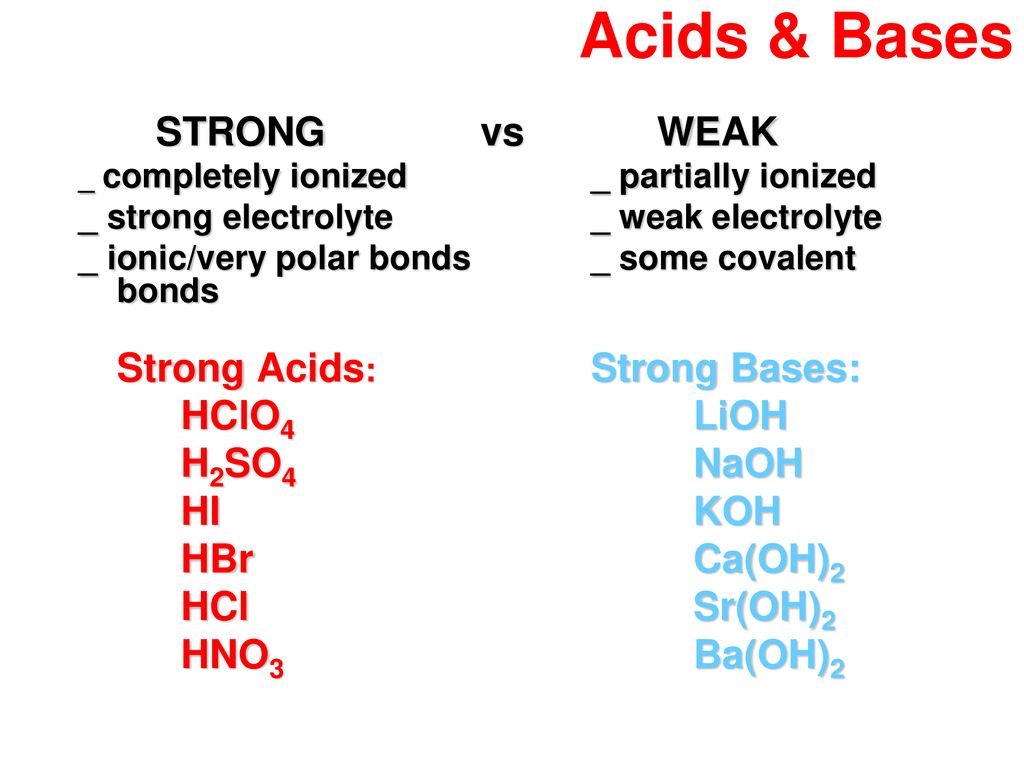
Weak Acids (= weak electrolytes) If the acid is not one of the strong acids above, you can safely assume it's a weak acid Note like the strong acid reactions given above, each reaction has water as a reactant, and the H is donated to it to form H 3O EXAMPLES FROM NOMENCLATURE THAT YOU NEED TO MEMORIZEHNO 2 Nitrous Acid HNO 2 W H NO1 seven strong acids HCl, HBr, HI, HNO 3, H 2SO 4, HClO 4, & HClO 3 2 solutions of strong acids have a high concentration of H 3 the molecular form of the strong acid does not exist in solution B Weak Acid dissolves but less than 100% dissociates to produce protons (H) 1 any acid that is not one of the seven strong is a weak acid (eAll strong bases are OH – compounds So a base based on some other mechanism, such as NH 3 (which does not contain OH − ions as part of its formula), will be a weak base Table 1 Some Common Strong acids and Strong Bases Strong Acids Strong Bases HClO 4 perchloric acid LiOH lithium hydroxide HCl hydrochloric acid



Difference Between Strong And Weak Acid Difference Between




Ppt Strong Acids Vs Weak Acids Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Solution Because HCl is listed in Table 122 "Strong Acids and Bases", it is a strong acid;Strong and Weak Acids and Bases 1 The following common acids are strong HCl, HBr, HI, HNO 3, HClO 4, H 2 SO 4 The following are some less common acids that are also strong HClO 3, HBrO 3, HIO 3, H 2 SeO 4 Assume all other acids are weak unless told otherwise Some weak acids HF, HNO 2, HClO 2, H 2 SO 3 = SO 2 H 2 O, HC 2 H 3 O 2 = HOAc 2HF is a weak acid From equation 1, you can see from the direction of the red arrow that HCl molecules donate hydrogen ions to H 2 O molecules Once they donate the proton, they form chloride ion (Cl – ), while H




Acids Bases Salts Ppt Download




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid
A strong acid is an acid where the pH is lower than, generally, 3 These acids are in very high concentration of H ions (an acid of pH 3 has 0001 moles per liter of H), while a weak acid's pH ranges from 3 to 7A very weak base always forms a strong conjugate acid As per BronstedLowry, HI is acid and loses one proton when combines with the water molecule and forms a base known as the conjugate base of an acid (HI) ∴ The conjugate base of HI is I –
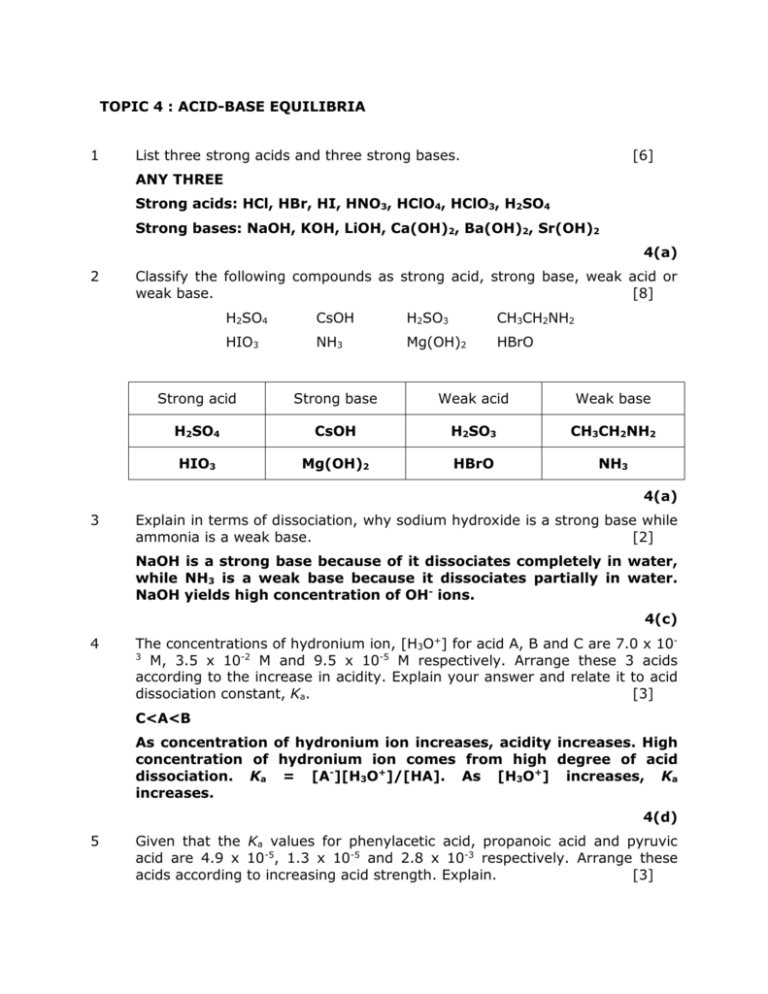



Topic 4 Acid Base Equilibria List Three Strong Acids And Three




Packet 10 Acids Bases And Salts Reference Tables K L M J T Ppt Download




Aleks Understanding The Difference Between Strong And Weak Acids Youtube




In Aqueous Solution Classify These Compounds As Strong Acids Weak Acids Strong Bases Weak Bases Or Homeworklib



14 3 Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Chemistry




Strength Of Acids Boundless Chemistry
/hydrofluoric-acid-molecule-147216065-5a7b7d47ba61770036b929f4.jpg)



Is Hydrofluoric Acid Hf A Strong Or Weak Acid



3



Which Is The Strong And Weak Acid In These Hf Hcl Hbr And Hi Quora



Solved Strong Acids Weak Acids Strong Bases Weak Bases Naoh Chegg Com



Acids And Bases When A Substance Dissolves In Water It Makes A Solution Solutions Can Be Sorted By Whether They Are Acid Basic Alkali Or Neutral Ppt Download




8 3 Strong And Weak Acids And Bases



Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria Ppt Download




Classify Each Of The Following Substances As Either A Strong Clutch Prep
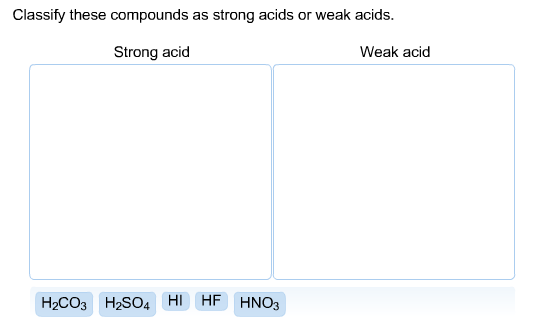



Solved Classify These Compounds As Strong Acids Or Weak Chegg Com




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid



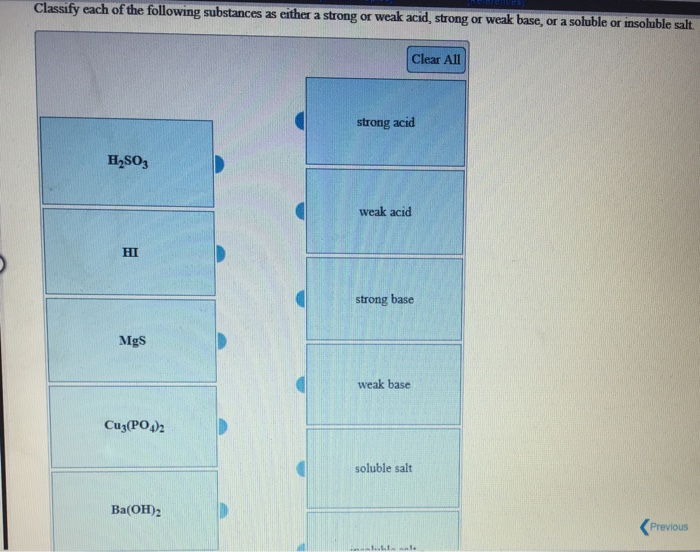
Solved Classify Each Of The Following Substances As Either A Strong Or Weak Acid Strong Or Weak Base Or A Soluble Or Insoluble Salt Course Hero




Why Is The Ka For Strong Acids So High But Weak Acids So Low Mcat
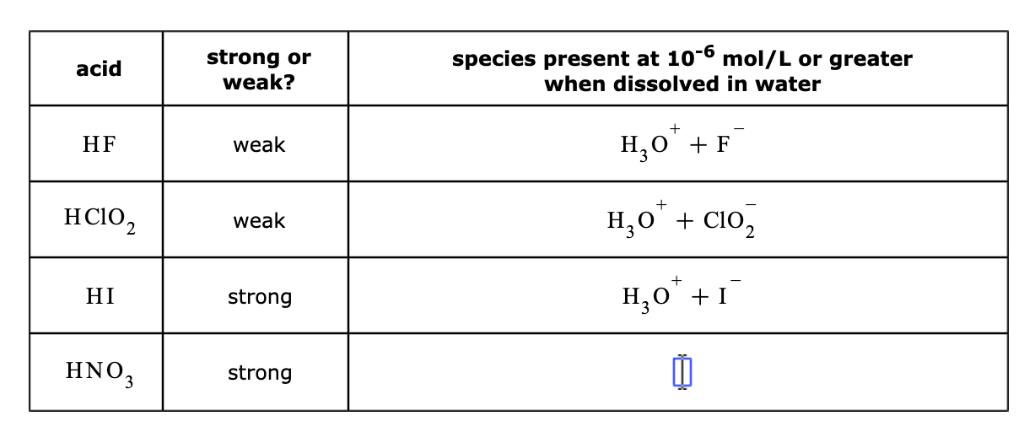



Solved Question 5 The Chemical Formulae Of Some Acids Are Chegg Com




How Many Of The Following Are Strong Acids Hbr Hclo3 H2so4 Hno2 Hi Hcn Hc2h3o2 Homeworklib
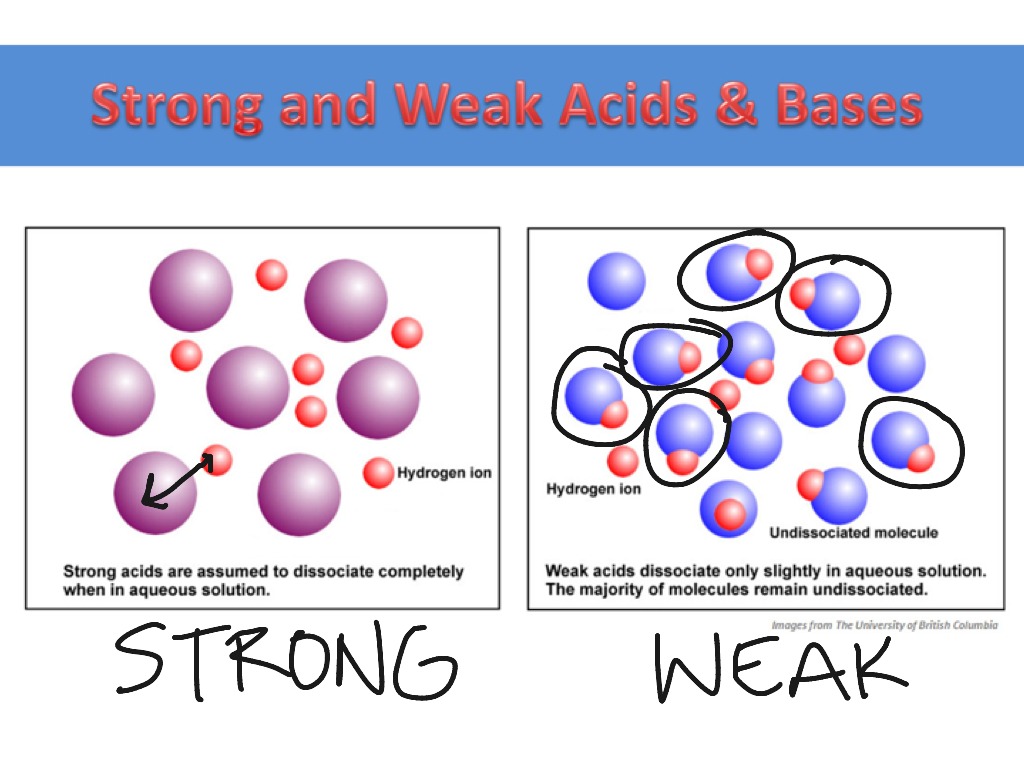



Strong And Weak Acids Bases Science Chemistry Showme
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)



What Are Strong Acids In Chemistry
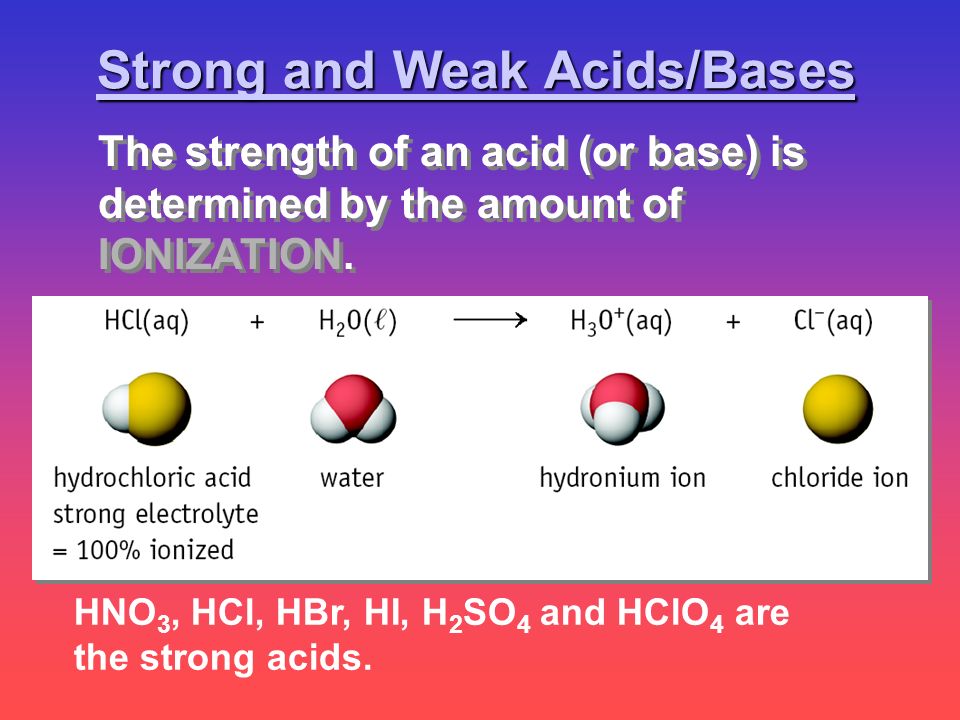



Hno 3 Hcl Hbr Hi H 2 So 4 And Hclo 4 Are The Strong Acids Strong And Weak Acids Bases The Strength Of An Acid Or Base Is Determined By The Amount Ppt Download




Lecture 9 Acid Base Equilibria I Strong Acids Hcl Hbr Hi Hno 3 H 2 So 4 Hclo 4 Ho N E O Weak Acid Ho N Eo 2 Strong Acid We Titrate With Strong Ppt Download



Strong Vs Weak Acids What S The Difference How Do They Dissociate The 7 Strong Acids Youtube




Chimie Amazing Common Strong And Weak Acids Instagram Chimie Amazing Link Www Instagram Com P Cb Fylrnmpa Igshid 1v9nmdhphnuhk Facebook




Strong And Weak Acids Bases Ppt Download




Acid Base Reactions Definitions Strong Acids Hcl Hbr Hi Hno 3 Hclo 4 H 2 So 4 Acid A Species That Supplies H Ions To Water Strong Acid Ppt Download




Titration Of A Strong Acid With A Strong Base Chemistry Libretexts




Acids And Bases I Introduction




Acids Bases




Key Gcc
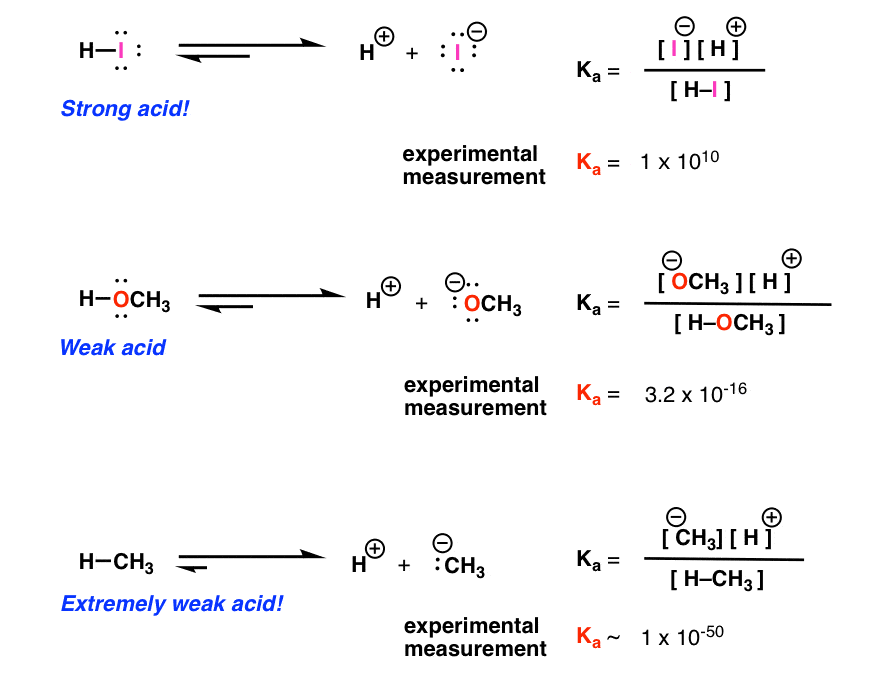



Acid Base Reactions Introducing Ka And Pka Master Organic Chemistry



Solved Why Is Hf A Weak Acid But At The Same Time Very Dangerous



3



What Are Some Examples Of Strong And Weak Acids And Bases Quora




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid
/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)



List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids



2



1




Solved Explain Why Hf Is A Weak Acid Whereas Hcl Hbr And Hi Are All Strong Acids



2
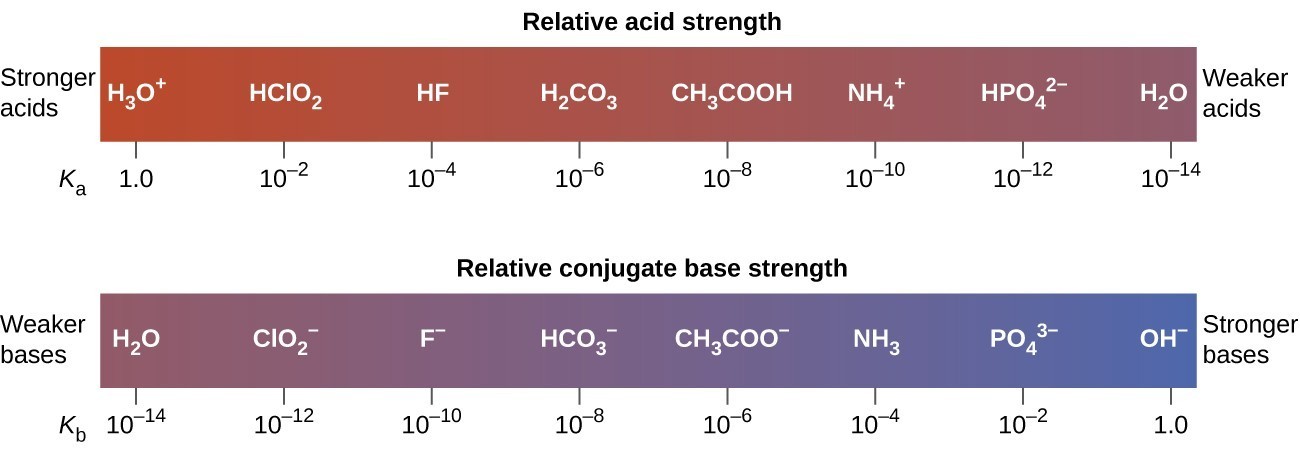



14 3 Percent Ionization And Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Chemistry




Strong And Weak Acids And Bases Biology



1




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid




In Aqueous Solution Classify These Compou Clutch Prep
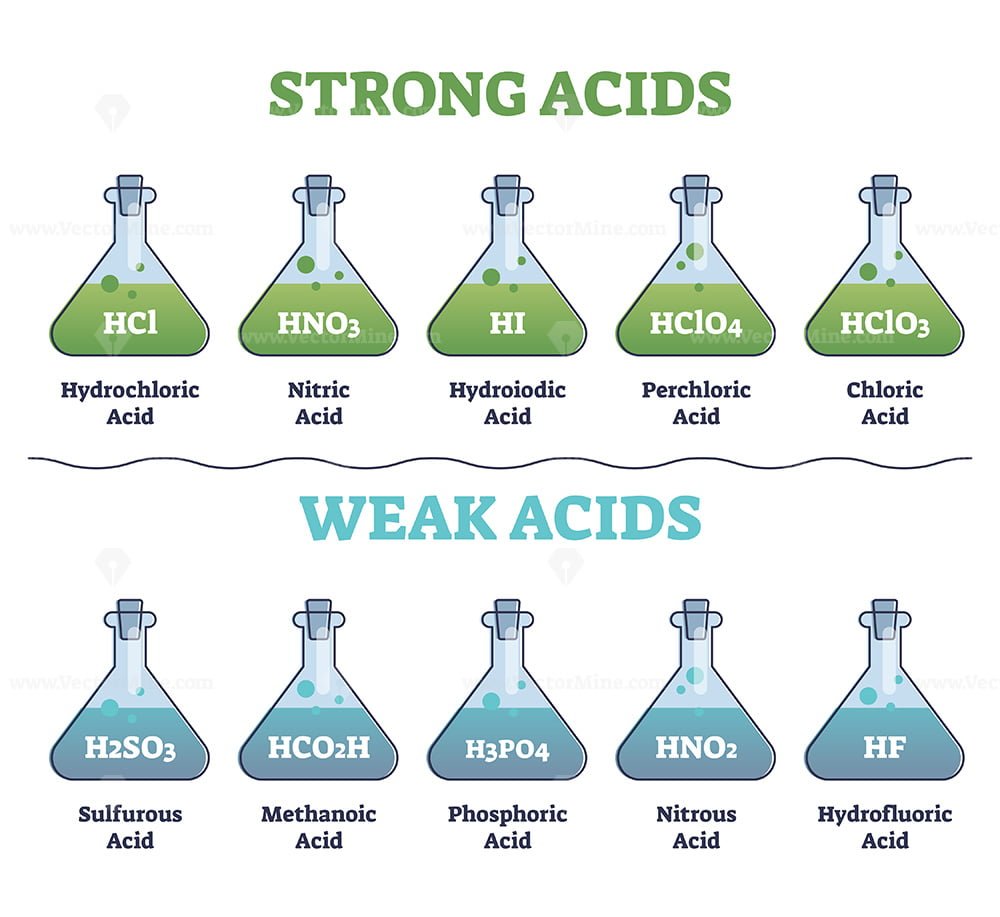



Strong And Weak Acids Collection With Educational Diagram Vectormine
/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)



List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids




2 1 16 Strong And Weak Acids Pearson Schools




Which Of The Following Compounds Is A Weak Acid Or W



Difference Between Strong And Weak Acids Definition Properties Examples




Strong Acids And Bases Overview Video Chemistry Ck 12 Foundation
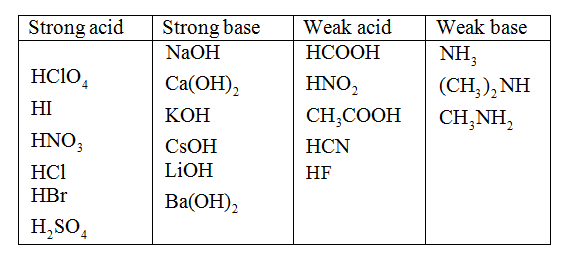



Classify Each Substance As A Strong Acid Strong Base Weak Acid Or Weak Base Home Work Help Learn Cbse Forum




Strong Acids And Bases Cheat Sheet Study Guide Mcat And Organic Chemistry Study Guides Tutoring








Strong And Weak Acids And Bases Numerade



What Are Strong And Weak Acids Example




Is Hydrofluoric Acid A Strong Or Weak Acid




Lecture 10 The Strong Acid Strong Base Equilibrium Calculation




Is Hi Hydroiodic Acid A Strong Or Weak Acid Youtube




Is Hi Hydroiodic Acid A Strong Or Weak Acid Youtube




Strong Weak Acids Bases Mr Carson S Science Page




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid




Www Nursing Journey Com Strong Or Weak Acids
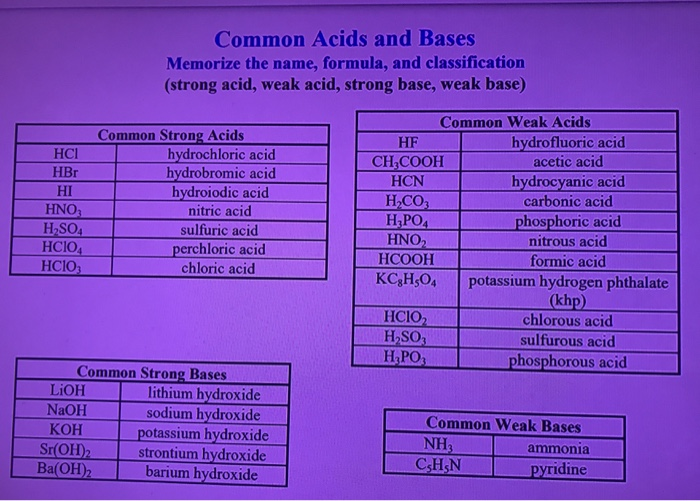



Solved Common Acids And Bases Memorize The Name Formula Chegg Com




Is Hi A Strong Acid Techiescientist
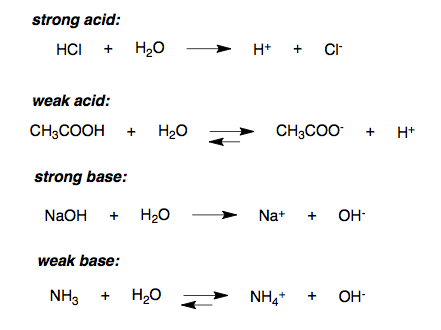



Strength Of Acids Boundless Chemistry
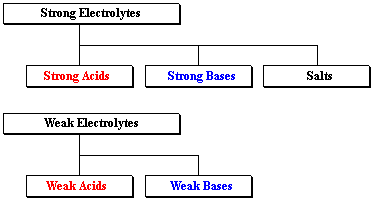



Classifying Electrolytes




Solved Hcl Hbr And Hi Are Strong Acids However Hf Is A Chegg Com



Solved So I M Pretty Sure I Have Hi Hcn Ba Oh 2 And Nh3 In The Right Places But I M Not Too Sure About H2so4 Csoh And H2so3 Can Someone Pleas Course Hero




List Of Strong Weak Acids Bases Chemistry Basics Chemistry Organic Chemistry




Strong And Weak Acids Bases Video Khan Academy




Classify These Compounds As Strong Acids O Clutch Prep
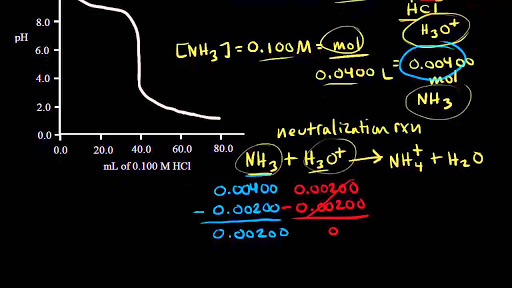



Titration Of A Weak Base With A Strong Acid Video Khan Academy




Is Hbr A Strong Or Weak Acid Youtube



Acids




Classify Each Substance As A Strong Acid Clutch Prep


