Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with − 1 1 in the expression f ( − 1) = ( − 1) 2 − 2 f ( 1) = ( 1) 2 2 Simplify the resultPrecalculus Find g (f (x)) f (x)=2x3 , g (x)=x1 f (x) = 2x − 3 f ( x) = 2 x 3 , g(x) = x 1 g ( x) = x 1 Set up the composite result function g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) Evaluate g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) by substituting in the value of f f into g g g(2x−3) = (2x−3)1 g ( 2 x 3) = ( 2 x 3) 1 Add −3The question needs to be made precise first One must clarify what mathf/math is supposed to be (a function from where to where?), and which are the numbers mathx/math for which the condition needs to hold (all numbers?

F X X 2 What Is G X A G X X 2b G X 2x 2c G X X 2 2d G X X 2 2 Brainly Com
F(x)=x^2 what is g(x) (2 2) brainly
F(x)=x^2 what is g(x) (2 2) brainly-Set up the composite result function Evaluate by substituting in the value of into Simplify each term Tap for more steps Rewrite as Expand using the FOIL Method Tap for more steps Apply the distributive property Apply the distributive property To find the inverse of a function, simply switch the x and y variables and solve for y Let's apply this concept to the first function given and see if we end up with the second function Also, note f (x) is basically y f (x) = x3 2 y = x3 2 First switch the variables x = y3 2 Now we need to solve for y, so isolate y




F X X2 What Is G X A G X 2 3 B X X2 C G X X2 3 D G X 3 2 Brainly Com
Find g (f (x)) f (x)=x^23x , g (x)=2x2 f (x) = x2 − 3x f ( x) = x 2 3 x , g (x) = 2x 2 g ( x) = 2 x 2 Set up the composite result function g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) Evaluate g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) by substituting in the value of f f into g g g(x2 − 3x) = 2(x2 − 3x)2 g ( x 2 3 x) = 2 ( x 2 3 x) 2 Simplify each term Answer f (x)*g (x) = (tan (x) 2/x) (x² 8) Apply FOIL in multiplying binomials Multiply the First terms, next is the Outer terms, then the Inner terms, and lastly, the Last terms = tan (x³) 8 tan (x) 2x²/x 2 (8)/x Simplifying we get = tan (x³) 8 tan (x) 2x 16/xAlgebra Find g (f (x)) f (x)=2x^23 , g (x)=3x2 f (x) = 2x2 3 f ( x) = 2 x 2 3 , g (x) = 3x − 2 g ( x) = 3 x 2 Set up the composite result function g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) Evaluate g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) by substituting in the value of f f into g g g(2x2 3) = 3(2x2 3)−2 g ( 2 x 2 3) = 3 ( 2 x 2 3) 2 Simplify each term
There's not enough information about f to answer that question But, taking the fact that it would be rare to have a function for a linear answer for increasing values of the input that is, it would be weird to note a function for such a simple Answer g(x) = 3x² Stepbystep explanation Since we have given that So, the function of g(x) would be since we have given that (1,3) on g(x means (x,ax) Here, x = 1 So, ax = 3 which implies that a = 3 So, g(x) would look like and the graph of g(x) is compressed 1814 views around the world You can reuse this answer Creative Commons License
Answer it is a operation of functions in multiplication actually there are 4 operations addition (fg) (x)=f (x)g (x) subtraction (fg) (x)=f (x)g (x) division f f (x)F f(x) = 2x2 and g(x) = 3x, what is (g o f)(x) a 6x2 b 9x2 c 18x2 d 8x4 Just add the two together (fg)(x)=(3x2)(x^21) (fg)(x)=x^23x1 Algebra Science Anatomy & Physiology



The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X X 2 What Is G X




If F X X 2 1 And G X X 5 Then G F X X 2 X Brainly Com
The graph of f(x)=x^2 is called a "Parabola" It looks like this One of the ways to graph this is to use plug in a few xvalues and get an idea of the shape Since the x values keep getting squared, there is an exponential increase on either side of the yaxis You can see this by plugging in a few values When x=0, f(x)=0 x=1, f(x)=1^2=1 x=2,f(x)=2^2=4 x=3, f(x)=3^2=9 x=4, f(x)=4^2 The rule (f ∘ g)(x) = f (g(x)) Replace g(x) by √x (f ∘ g)(x) = f (√x) For any input (u), f gives (u)2, so f (√x) = (√x)2 But (√x)2 = x So we finish with (f ∘ g)(x) = x where x is in 0∞)Justine graphs the function f(x) = (x 7)2 1 On the same grid, she graphs the function g(x) = (x 6)2 3 Which transformation will map f(x) on to g(x)?




If F X 5x 2 And G X 2x 1 Find F G X Brainly Com




What Is F G X F X X 2 36 G X X 3 2x 2 10 Enter Your Answer In The Box Brainly Com
a^33a^2 Given f(x)=x^2,g(x)=x3 (f*g)(x)=x^2(x3) =x^33x^2 (f*g)(a)=(a)^33(a)^2 =a^33a^2 Let #f(x)=x^2# and #g(x)=x3# What is the value of #(f*g)(a Denominator (3x)=0 x=3 This means at x=3 function is not defined And by definition of domain The domain is where the function is not defined Domain is Range Put f(x)=y Range is the set of value that correspond to domain Equate the denominator to zero Denominator (y1)=0 y=1 This means at y=1 function is not defined Range isInverse\y=\frac{x}{x^26x8} inverse\f(x)=\sqrt{x3} inverse\f(x)=\cos(2x5) inverse\f(x)=\sin(3x) precalculusfunctioninversecalculator en Related Symbolab blog posts Functions A function basically relates an input to an output, there's an input, a relationship and an output For every input




If F X X 2 2 And G X 2x 2 X 3 Find F G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 3f X Brainly Com
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreReplace the x in the f(x) equation with the value of g(x) to get (x3)cubed 2That's it When you write f(x) = x3 2 That means x can be any number, equation or function and whatever that value is, it goes into x3 2Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor




Urgent F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X 2x 2 1 1 And G X X 2 7 Find F G X Brainly Com
G(x), however, was the dependent variable in another equation, so it's value had to be calculated before you could put it into f(g(x)) that's exactly what we did above we solved for g(2) to get 7 then we solved for f(g(x)) to get f(7) = 3 you are placing g(x) into the argument of the equation f(x) = sqrt(x2) which means you are replacingGraph f (x)=2x^2 f (x) = −2x2 f ( x) = 2 x 2 Find the properties of the given parabola Tap for more steps Rewrite the equation in vertex form Tap for more steps Complete the square for − 2 x 2 2 x 2 Tap for more steps Use the form a x 2 b x c a x 2 b xTo find inverse function, just try getting x from the original function For example, inverse of f (x) = ln (x 2 ) would be f (x) = e x/2 Thus, If g (f (x)) = x, that means f (x) = g 1 (x) = (x2)/3 So, f (2) = (2 – 2)/3 = 0 2 level 1 cover 2 years ago There's always a simpleashell way to do these




Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X F 5x Can Some Please Help Me Brainly Com




Suppose F X X2 What Is The Graph Of G X F 2x Brainly Com
See first you have to calculate g(1) which is g(1) = (1)^2 2 g(1) = 1–2 = 1 g(1) = f(g(1)) = f(1) Now we will calculate required value of f(g(1)) f(gLeft 13 units, down 2 units right 13 units, down 2 units left 13 units, up 2 units right 13 units, up 2 units For two given functions f(x) and g(x), the function (f g)(x) is (f g)(x) = f(x) g(x) Here we have the functions f(x) = x^2 1 g(x) = 5 x Now we want to find (f g)(x), we can use the above expression (f g)(x) = f(x) g(x) = (x^2 1) (5 x) (f g)(x) = x^2 1 5 x = x^2 x 6 (f g)(x) = x^2 x 6




F X X 2 What Is G X A G X X 2 4 B G X X 2 4 C G X 4x 2 D G X X 2 4 Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X A G X X 2b G X 2x 2c G X X 2 2d G X X 2 2 Brainly Com
2x² 17x 35 26x² x 15 find the tenth term of the arithmetic sequence if the first term is 6 and the common difference is 2 find fg , fg , fg and f/g f(x) =1/2x , g(x) = 2/x12A composite function is a function which is made by combining two or more than two functions For example, if f(x) f ( x) and g(x) g ( x) are two functions, then we can define two composite =x f(g(x))=2(x1)/21 =x11 =x




Given F X 2 X And G X X 1 Fog X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
Find f(g(x)) f(x)=x^24 ;Composite Functions – Explanation & Examples In mathematics, a function is a rule which relates a given set of inputs to a set of possible outputs The important point to note about a function is that each input is related to exactly one output The process of naming functions is known as function notation TheAxis of Symmetry x = 2 x = 2 Directrix y = −9 4 y = 9 4 Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with 1 1 in the expression f ( 1) = ( 1) 2 − 4 ⋅ 1 2 f ( 1) = ( 1) 2 4 ⋅ 1 2




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
F (g (2)), g (x)=2x1, f (x)=x^2 \square!G (x) is not actually defined at x=2 so we can't ask about its continuity or derivative at that x value For f (x) yes your reasoning is sound g ( x ) is not actually defined at x = 2 so we can't ask about its continuity or derivative at that x valueExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music




Suppose That F X X2 And G X 3x2 8 Which Statement Best Compares The Graph Of G X With The Brainly Com




For F X 2x 1 And G X X 2 7 Find F G X A 3x 2 7x 6 B 2x 2 13c 2x 2 X 2 14x 7d 2x 2 Brainly Com
Graph f (x)=2 f (x) = 2 f ( x) = 2 Rewrite the function as an equation y = 2 y = 2 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept y = m x b y = m x b Find the values of m m and b b using theGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Start studying Evaluating Functions Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools



F X X 2 What Is G X 1 9




For F X 3x 1 And G X X 2 6 Find F G X Brainly Com
f(g(x))=sqrt(x^42 and g(g(x))=x^4 As f(x)=sqrt(x^22) and g(x)=x^2 f(g(x))=sqrt((g(x))^22)=sqrt((x^2)^22) = sqrt(x^42 and g(g(x))=(x^2)^2=x^4G(x) → "g of x" → "operation(s), g, applied to a given quantity or value , x" "g(x) = x1" tells you to simply subtract 1 from whatever xvalue is given g(5)= 5–1=4 g(6)= 6–1=5 g(9)= 9–1=8 g(x)=x1 f(x) → "f of x" → "operations, f, applied to a gLearn how to solve f(g(x)) by replacing the x found in the outside function f(x) by g(x)




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Consider The Function F X 3x 2 And The Function G X Which Is Represented By The Table Below Brainly Com




F X X 2 Which Of These Is G X Please Help Asap Brainly Com




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Suppose That F X X2 And G X 2 3 X 2 Which Statement Best Compares The Graph Of G X With The Brainly Com



F X X 2 What Is G X Apex




If F X 3x 2 4 And G X X 2 Find F G X Brainly Com




Please Help Suppose That F X X 2 And G X 3x 2 8 Which Statement Best Compares The Graph Of G X Brainly Com



Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 3f X




Find F G X When F X X 2 7x 12 And G X 7 X 2 16 Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X X2 And G X X 1 Then F G X Brainly Com




F X X2 What Is G X A G X 2 3 B X X2 C G X X2 3 D G X 3 2 Brainly Com




Find The Domain Of F G X Where F X X 2 And G X 3 X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X 2x 2 3 And G X X 2 7 Find F G X Brainly Com




Suppose F X X 2 And G X 7x 2 Brainly Com




F X 2x3 3x2 7x 2 G X 2x 5 Find F G X Brainly Com




The Graph Of G X X 2 2 Is A Translation Of The Graph Of F X Up Down Left Right By Units Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X X 2 1 And G X X 5 Then G F X X 2 X Brainly Com




For All Values Of X F X 2x 6 And G X X2 2 A Find G 3 B Find Fg 3 Brainly Com




The Graph Of Fx Shown Below Resembles The Graph Of G X X2 But It Has Been Changed Somewhat Brainly Com




Please Help Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X F 3x Brainly Com
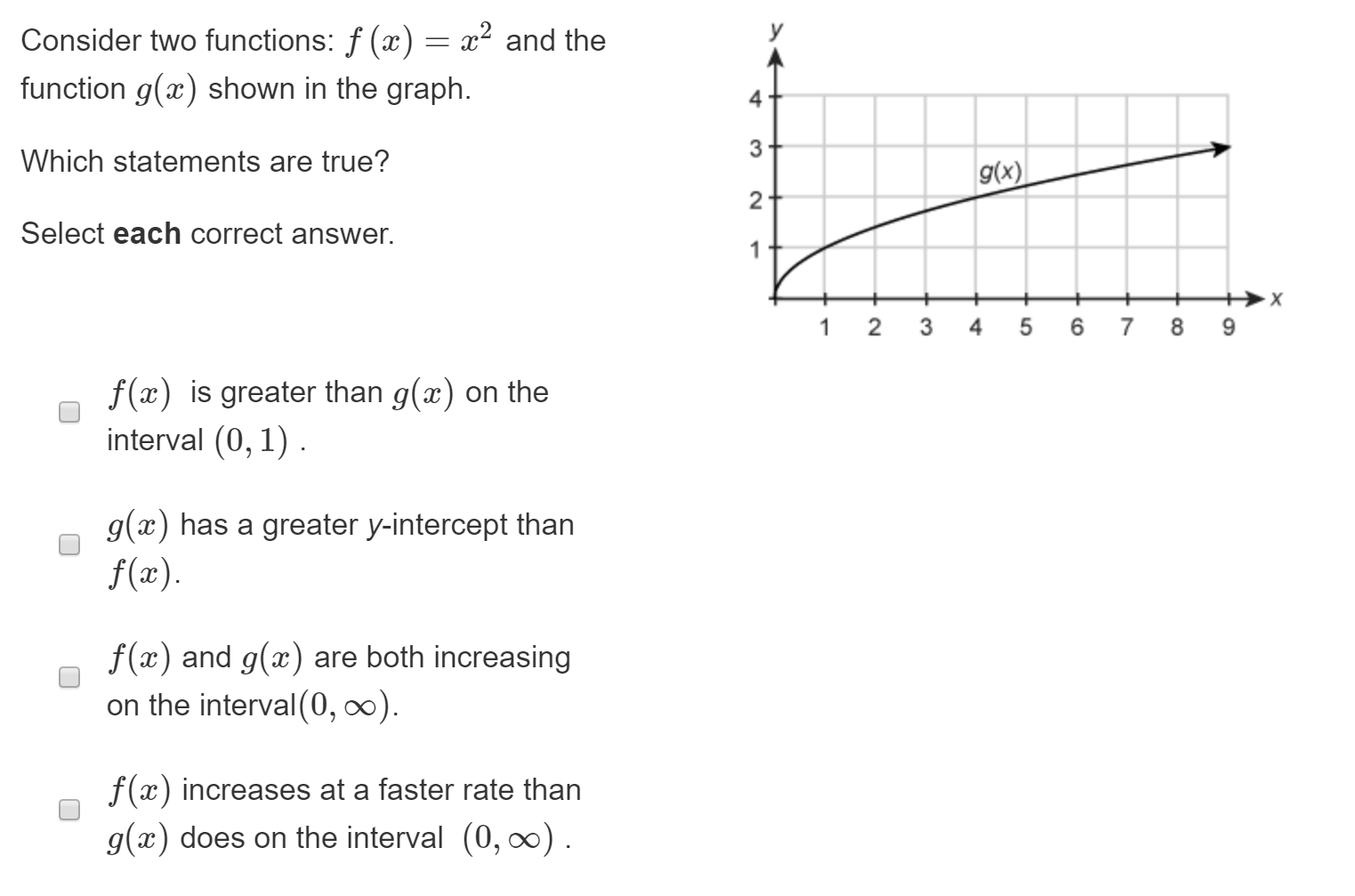



Y Consider Two Functions F X X2 And The Function Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




For F X 4x 1 And G X X 2 5 Find F G X O A 4x2 19 O B 4x3 X2 4x 6 O C 4x3 X2 Brainly Com




The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X X 2 What Is G X A G X X 2 3 B Brainly Com




Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 2 F X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X 3x 2 6x 5 G X 4x 3 5x 2 6 Find F G C Brainly Com




The Graph Of F X Shown Below Resembles The Graph Of G X X 2 But It Has Been Changed Somewhat Brainly Com




Please Help Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 4 F X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




The Graph Of F X Shown Below Has The Same Shape As The Graph Of G X X 2 But It Is Shifted Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Suppose F X X 2 And G X 1 5x 2 Which Statement Best Compares The Graph Of G X With The Graph Brainly Com




Help Please Consider These Functions F X 5x2 2 G X X2 1 What Is The Value Of G F 1 A Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X 0 5x 2 2 And G X 8x 3 2 Brainly Com




If F X X2 And G X X 1 Then G F X X 2 Brainly Com




F X 3x 2 5 G X 4x 2 H X X 2 3x 1 Find F X G X H X A 7x 2 X 4 B 2x 2 X 2 C 2x 2 7x 2 D 5x 2 4 Brainly Com




Let F X Log X 2 2x And G X X X 1 Which Expression Represents Fog X Brainly Com




The Graph Of F X Shown Below Resembles The Graph Of G X X 2 But It Has Been Changed Brainly Com
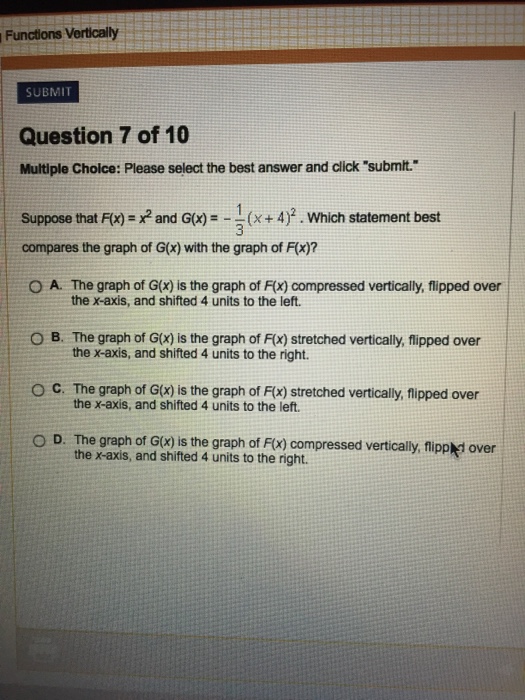



Suppose That F X X 2 And G X 1 3 X 4 2 Which Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Given F X 2x 5 And G X X2 And H X 2x H G X X X Brainly Com




Suppose That G X F X 2 Which Statement Best Compares The Graph Of G X With The Graph Of F X A Brainly Com




The Graph Of G X Resembles The Graph Of F X X2 But It Has Been Changed Which Of These Is The Brainly Com




The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X X What Is G X Brainly Com




If X X 2 2 And G X 2x2 X 3 Find F G X Brainly Com




Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X F 2x Brainly Com




F X 2x 2 3 And G X X 2 7 Find F G X Brainly Com




F 4 If G X 2 X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X X And G X 2 What Is F G X Brainly Com




If F X X 2 6x 1 And G X 3x 2 4x 1 Find F G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X 3x 1 And G X X 2 Find F G X Brainly Com




The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X X What Is The G X A G X X 2 2 B Brainly Com




Solved F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Please Help For All Values Of X F X X 1 And G X 2x 2 3 Solve Fg X Gf X Brainly Com




Please Answer Asap Let F X 3 2x And G X 1 2 X 1 Graph The Functions On The Same Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Helppp The Graph Of F X Shown Below Resembles The Graph Of G X X 2 But It Has Been Brainly Com




The Functions Fx And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Help Me If F X X 2 1 And G X 2x 3 What Is The Domain If F G X Brainly Com




F 4 If G X 2 X Brainly Com




Solved The Functions F X And G X Are Shown In The Graph F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X 2x 2 1 And G X X 2 7 Find F G X Brainly Com




F X X2 What Is G X F X G X 2 2 15 Brainly Com




F X X 2 3x 2 Is Shifted 2 Units Left The Result Is G X What Is G X Brainly Com




For F X 3x 1 And G X X2 6 Find G F X Brainly Com




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Please Help Me F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com


